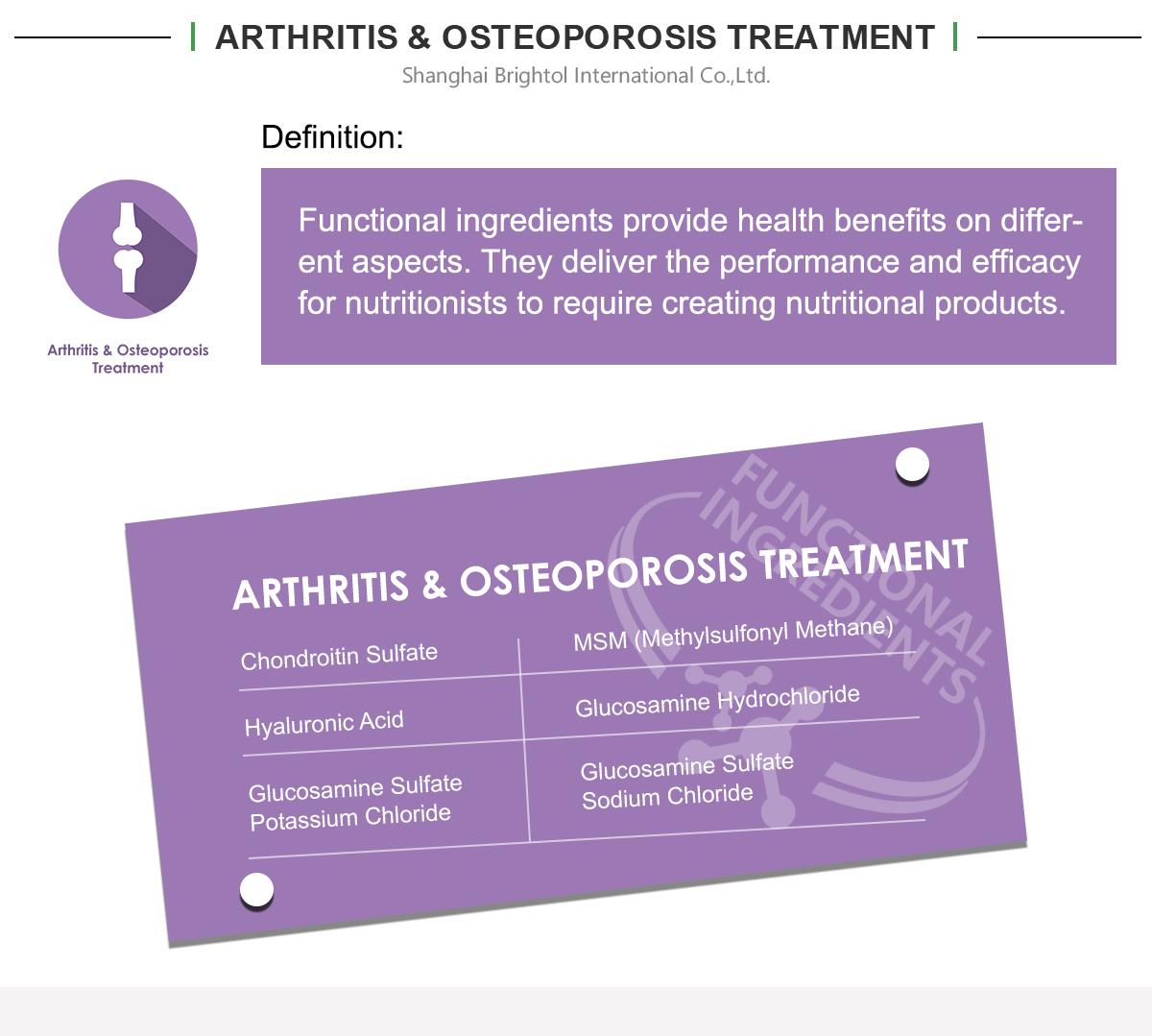
Product Name: Chondroitin Sulfate
Synonyms:Poly-1(2/3)-N-acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-3-O-beta-
D-glucopyranurosyl-4-(6)sulfonyl-D-galactose
Molecular Formula: (C14H21NO14S)n
CAS No.: 9007-28-7
EINECS: 232-696-9
Description:
Chondroitin sulfate, also called chondroitin sulphate, is a useful nutritional adjunct for individuals who wish to support the structure and function of the body’s connective tissues, such as skin, tendons, ligaments, bone, and cartilage.


Product Name: Chondroitin Sulfate
Synonyms:Poly-1(2/3)-N-acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-3-O-beta-
D-glucopyranurosyl-4-(6)sulfonyl-D-galactose
Molecular Formula: (C14H21NO14S)n
CAS No.: 9007-28-7
EINECS: 232-696-9
Description:
Chondroitin sulfate, also called chondroitin sulphate, is a useful nutritional adjunct for individuals who wish to support the structure and function of the body’s connective tissues, such as skin, tendons, ligaments, bone, and cartilage.
Uses:
Joint Support: The glycosaminoglycan chondroitin sulfate is one of the most vital compounds in connective tissue responsible for building and supporting the ground substance of cartilage. Research suggests that it may also protect cartilage by moderating healthy enzyme activity.
Benefits:
1.Chondroitin sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan formed naturally by the body for the synthesis and maintenance of connective tissue.
2.Glycosaminoglycans, formerly termed mucopolysaccharides, are an integral component of all connective tissues.
3.Connective tissues have various functions in the body. They support internal organs and connect bones to each other (ligaments), form bone, cartilage, and the walls of blood vessels, attach muscles to bones (tendons), and replace tissues that have been damaged. The two primary components of connective tissue are collagen and proteoglycans.
4.Collagen is the strong, fibrous protein that physically connects our tissues. Proteoglycans are large carbohydrate-rich structures, resembling a bottle-brush in the three-dimensional structure, i.e. a central protein rod with many strings of glucosamine-containing glycosaminoglycans extending outwards.
5.Proteoglycans hold large amounts of water forming a stiff gel by virtue of their dense negative charges from sulfates. Proteoglycans link to collagen fibers to help form connective tissues. They provide resiliency, load distribution, shock-absorbing, compressive, and lubricating properties to connective tissues and joints.
6.Chondroitin sulfate is supportive and protective of connective tissues in numerous ways. It is an excellent source of n-acetylgalactoaminoglycan for the synthesis and protection of proteoglycans associated with cartilage tissues.