Vitamin B5
Introduction:
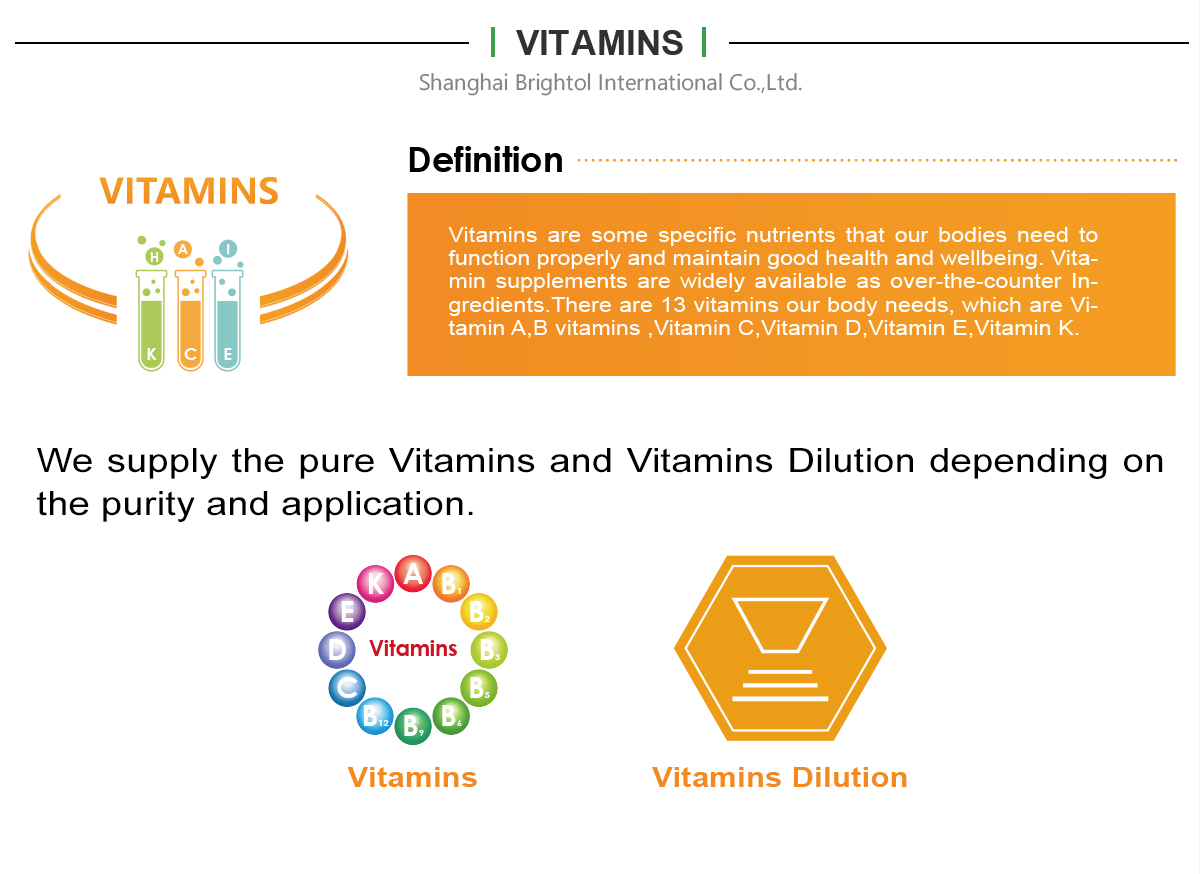
Vitamin B5, also called pantothenic acid, is one of the most important vitamins for human life. It’s necessary for making blood cells, and it helps you convert the food you eat into energy.
D-calcium Pantothenic is kind of white powder, odorless, slightly hygroscopic. It taste a little bitter. Its aqueous solution shows neutral or faintly base. It is part of Coenzyme A and widely used in medicine, food and feed industry.

 Vitamin B3 (Niacinamide)
Vitamin B3 (Niacinamide)
Introduction:
Niacinamide, also known as nicotinamide and nicotinic amide, is the biosynthesized form of niacin, commonly known as vitamin B3. Both forms provide the same vitamin functions, Niacin normally enters the body through dietary sources, which is then converted into niacinamide. The primary biochemical uses of niacinamide are the synthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), which are enzymes in a variety of oxidation-reduction reactions. Nicotinamide is an essential water-soluble vitamin, which is not synthesized in the body.
Vitamin B5
Introduction:
Vitamin B5, also called pantothenic acid, is one of the most important vitamins for human life. It’s necessary for making blood cells, and it helps you convert the food you eat into energy.
D-calcium Pantothenic is kind of white powder, odorless, slightly hygroscopic. It taste a little bitter. Its aqueous solution shows neutral or faintly base. It is part of Coenzyme A and widely used in medicine, food and feed industry.
Pantothenate is the most biologically active form of vitamin B5 in humans. However, pantothenate must be broken down into pantothenic acid before it can be absorbed. Pantothenic acid exists in two stereoisomers, including dextrorotatory (D) and levorotatory (L) forms. Only D-pantothenic acid is biologically active, while L-pantothenic acid may inhibit the action of the D isomer.
Identification
|
Name |
Calcium pantothenate |
|
Molecular Formula |
C18H32CaN2O10 |
|
Molecular Weight |
476.54 |
|
CAS NO. |
137-08-6 |
|
EINECS |
205-278-9 |
|
Melting point |
190 ºC |
|
Alpha |
26.5 º (c=5, in water) |
Function:
Energy support
Vitamin B5 can help to maintain energy levels in a variety of ways. These include the conversion of food to chemical energy, red blood cell production and the synthesis of hormones in the adrenal gland.
Healthy cholesterol level management
Vitamin B5 may help to maintain a healthy cholesterol profile, according to some studies. The specific components of this profile include HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
Joint health support
Some evidence suggests that vitamin B5 supplements may help to manage joint discomfort and morning stiffness.
Supports wound repair
Supplements of vitamin B5 may also support wound healing, especially after surgery.
Specification
|
Items |
Standard |
|
Assay(in dry products) |
98.0~101.0% |
|
Calcium content |
8.2~8.6% |
|
Nitrogen content |
5.7~6.0% |
|
Specific rotation |
+25.0º~+28.5º |
|
Heavy metals(Pb) |
≤0.002% |
|
Loss on drying |
≤5.0% |
|
Methanol |
≤0.3% |