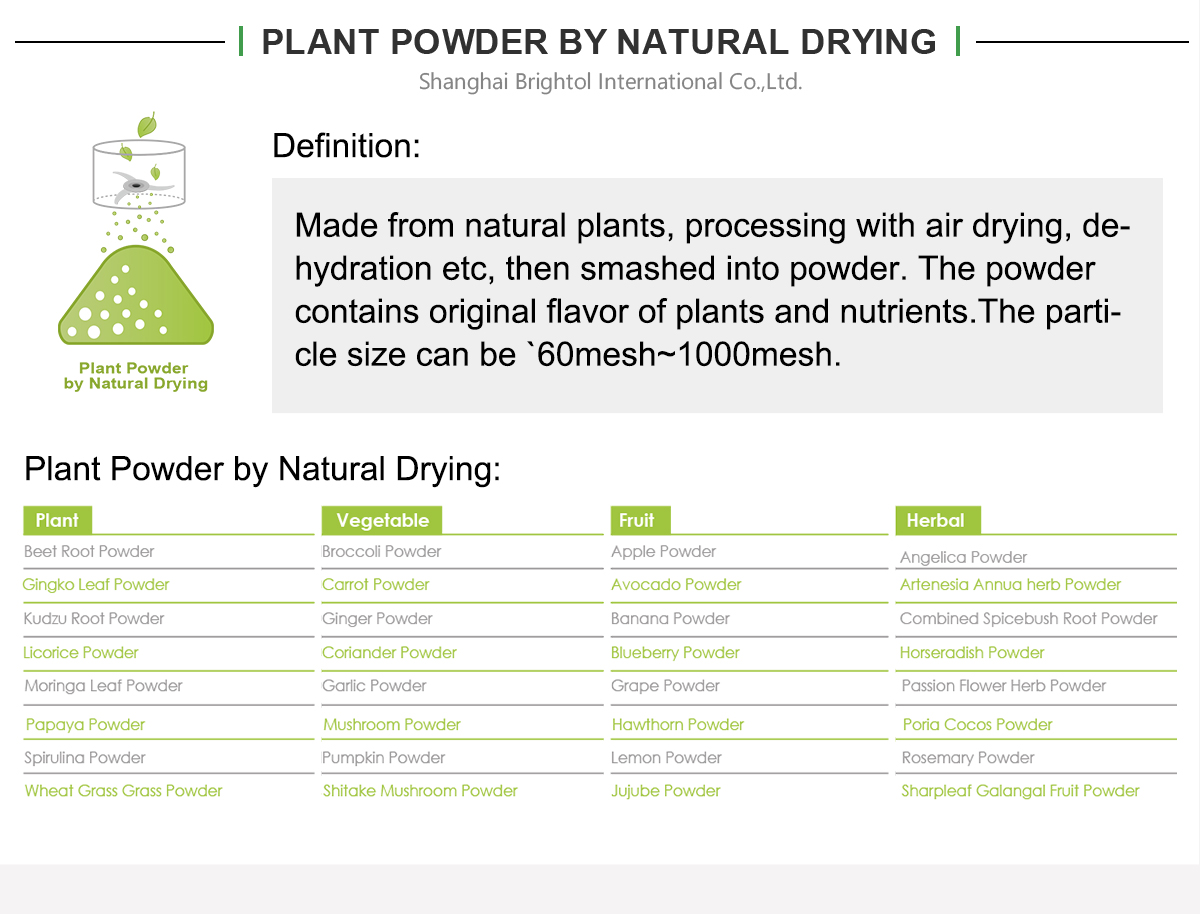
Description
Peony is a flowering plant native to Asia, Europe and Western North America. They are among the most popular garden plants in temperate regions, with 40 distinguished species. Mostly are herbaceous perennial plants up to 1 meter tall, but some are woody shrubs can stretch up to 3.5 meters tall.
They have deeply lobed leaves and large, often fragrant flowers, in colors ranging from purple red to white or yellow, flowering from late spring. Peonies are usually propagated by root division, but also by grafting, division, seed, and from cuttings.

 Description
Description
Peony is a flowering plant native to Asia, Europe and Western North America. They are among the most popular garden plants in temperate regions, with 40 distinguished species. Mostly are herbaceous perennial plants up to 1 meter tall, but some are woody shrubs can stretch up to 3.5 meters tall.
They have deeply lobed leaves and large, often fragrant flowers, in colors ranging from purple red to white or yellow, flowering from late spring. Peonies are usually propagated by root division, but also by grafting, division, seed, and from cuttings.
Culinary Use Of Peony
In China, the fallen petals of Paeonia lactiflora are parboiled and sweetened as a tea-time delicacy. Peony water, an infusion of peony petals, makes a refreshing drink, common since middle ages. The petals may be added to salads or to punches and lemonades. Its fresh top young leaves, same as for Camellia and rose plants, are excellent for making white tea.
Medicinal Properties of Peony
Peony root are diuretic, sedative, and tonic. the plant is known for its antispasmodic, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory effects. Greeks used it to treat epilepsy and promote menstruation. European herbalists used the root as an antispasmodic and to soothe nerves. In Chinese medicine, White Peony was used to treat hypertension, chest pain, muscle cramping and spasms, as well as for a fever. Nowadays is still the most widely used herbs to treat menstrual cramps and menstrual irregularities.
Peony contains 18 active constituents responsible for inhibiting blood coagulation or platelet aggregation. The active constituents include paeoniflorin, catechin and paeonol. The anti-coagulant effect of peony supports healthy blood circulation, which prevents against certain cardiovascular diseases.