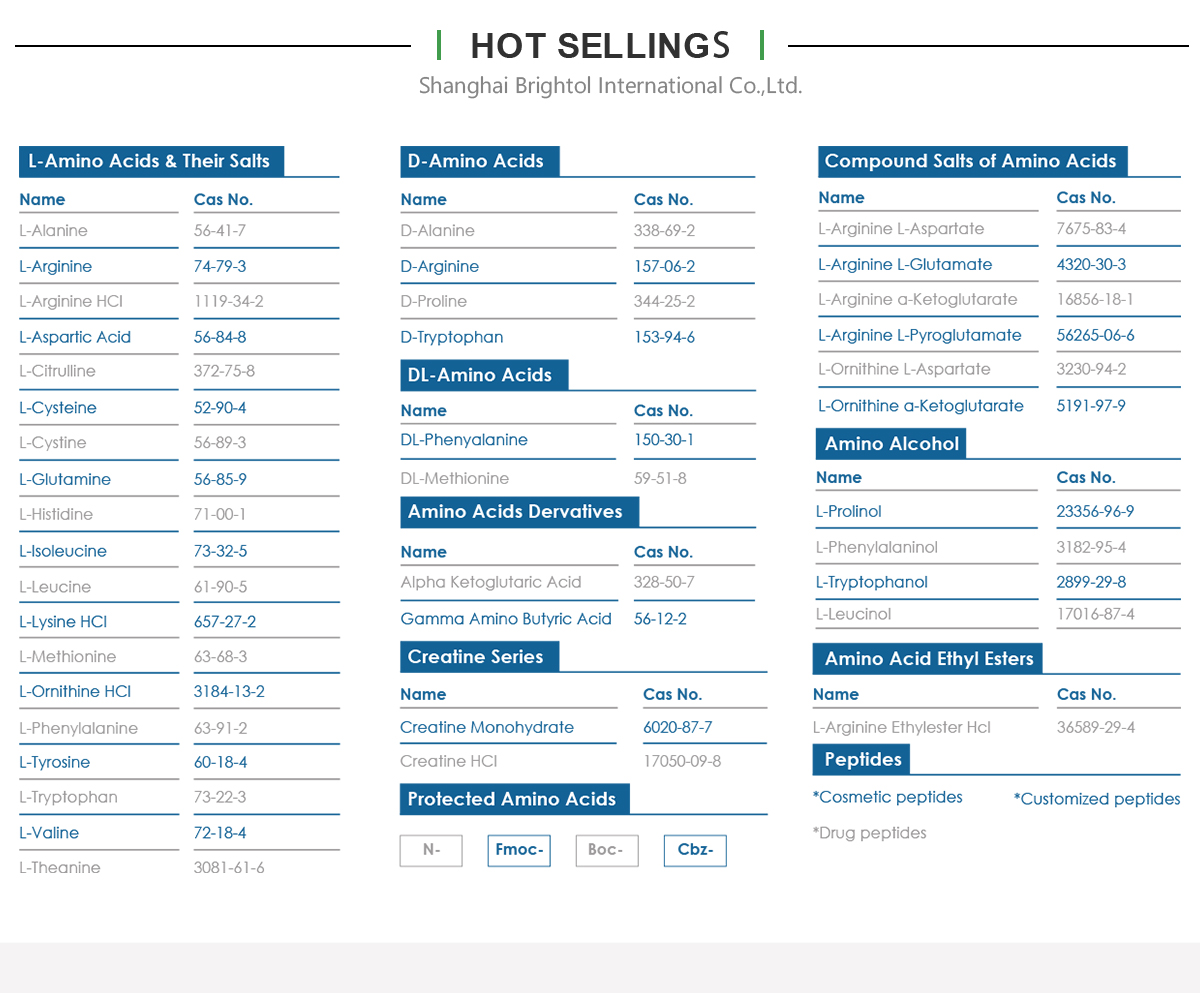
Product Name: L-Aspartic Acid
Synonyms: L(+)-Aspartic acid;
L-2-Aminobutanedioic acid; L-Aminosuccinic acid
Molecular Formula: C4H7NO4
Molecular Weight: 133.10
CAS No.: 56-84-8
EINECS: 200-291-6
Description
L-aspartic acid, often just called aspartic acid, is an amino acid — the building block of proteins and necessary for several other processes in the body. For instance, you can burn amino acids for energy, convert them into fat and other molecules, or use them to make your own cellular proteins.


Product Name: L-Aspartic Acid
Synonyms: L(+)-Aspartic acid;
L-2-Aminobutanedioic acid; L-Aminosuccinic acid
Molecular Formula: C4H7NO4
Molecular Weight: 133.10
CAS No.: 56-84-8
EINECS: 200-291-6
Description
L-aspartic acid, often just called aspartic acid, is an amino acid — the building block of proteins and necessary for several other processes in the body. For instance, you can burn amino acids for energy, convert them into fat and other molecules, or use them to make your own cellular proteins.
Aspartic acid (Asp, D), also known as aspartate, the name of its anion, is one of the 20 natural proteinogenic amino acids which are the building blocks of proteins. As its name indicates, aspartic acid is the carboxylic acid analog of asparagine. As a neurotransmitter, aspartic acid may provide resistance to fatigue and thus lead to endurance.
Uses
Like all amino acids, your body can use aspartic acid to provide your cells with energy; the cells burn it to generate ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, which is a cellular energy currency.
Benefits
1) Energy and glucose production
2) Memory and cognition
3) Immune function
4) Reproduction
5) Removal of toxins