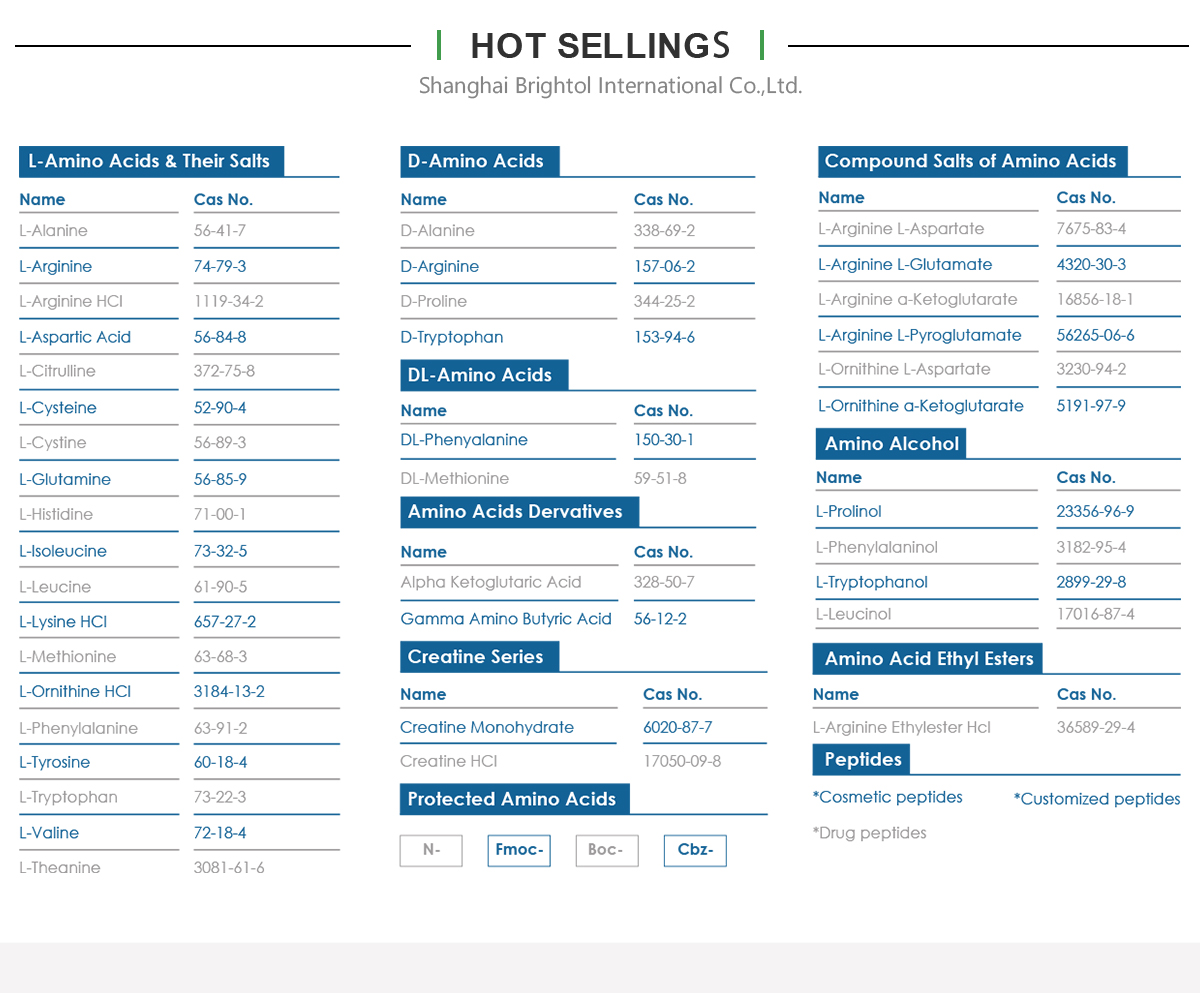
Product Name: L-Arginine alpha-ketoglutarate (2:1)
Synonyms: L-Arginine 2-oxopentanedioate
Molecular Formula: 2(C6H14N4O2).C5H6O5
Molecular Weight: 530.53
CAS No.: 5256-76-8
EINECS: 226-059-4
Description
L-arginine alpha ketoglutarate, shortened simply to AAKG, is comprised of two important compounds to your health. Arginine is a semi-essential or conditionally essential amino acid, meaning that it is necessary to proper health and bodily functions but can only be created in the body under specific situations. Normally, it comes from supplements or from diet sources, including soy beans, peanuts, pumpkin seeds, dairy products, and poultry and other lean cuts of meat. Alpha ketoglutarate is an important compound created during the Krebs cycle, which breaks down molecules to create a pool of energy.


Product Name: L-Arginine alpha-ketoglutarate (2:1)
Synonyms: L-Arginine 2-oxopentanedioate
Molecular Formula: 2(C6H14N4O2).C5H6O5
Molecular Weight: 530.53
CAS No.: 5256-76-8
EINECS: 226-059-4
Description
L-arginine alpha ketoglutarate, shortened simply to AAKG, is comprised of two important compounds to your health. Arginine is a semi-essential or conditionally essential amino acid, meaning that it is necessary to proper health and bodily functions but can only be created in the body under specific situations. Normally, it comes from supplements or from diet sources, including soy beans, peanuts, pumpkin seeds, dairy products, and poultry and other lean cuts of meat. Alpha ketoglutarate is an important compound created during the Krebs cycle, which breaks down molecules to create a pool of energy.
When combined, alpha ketoglutarate has actually been shown to increase the intestinal uptake of arginine. AAKG presents a wide range of potential benefits and uses that may improve your health and wellbeing.
Uses and benefits
AAKG benefits most commonly involve supplementation for bodybuilding and athletic performance. Studies suggest that AAKG may effectively help the liver neutralize ammonia and other harmful substances, which should make for less pain, less muscle fatigue, and longer workouts. Arginine may also be beneficial for its role in building protein. Creating various protein chains is necessary for developing larger, stronger muscles and repairing damaged muscle tissue. In studies, arginine has also been associated with increased insulin production. Increased insulin has been found to assist in creating greater muscle growth and strength.
Arginine is also prized for its potential to increase nitric oxide activity. Increased nitric oxide production may lead to wider blood vessels, which in turn may result in increased blood flow. This means more oxygen and nutrients to muscles and organs. Wider blood vessels also means more carbohydrates, protein chains, and muscle building hormones. All of this may result in greater physical performance, enhanced workout capacity, improved endurance, and reduced recovery times.