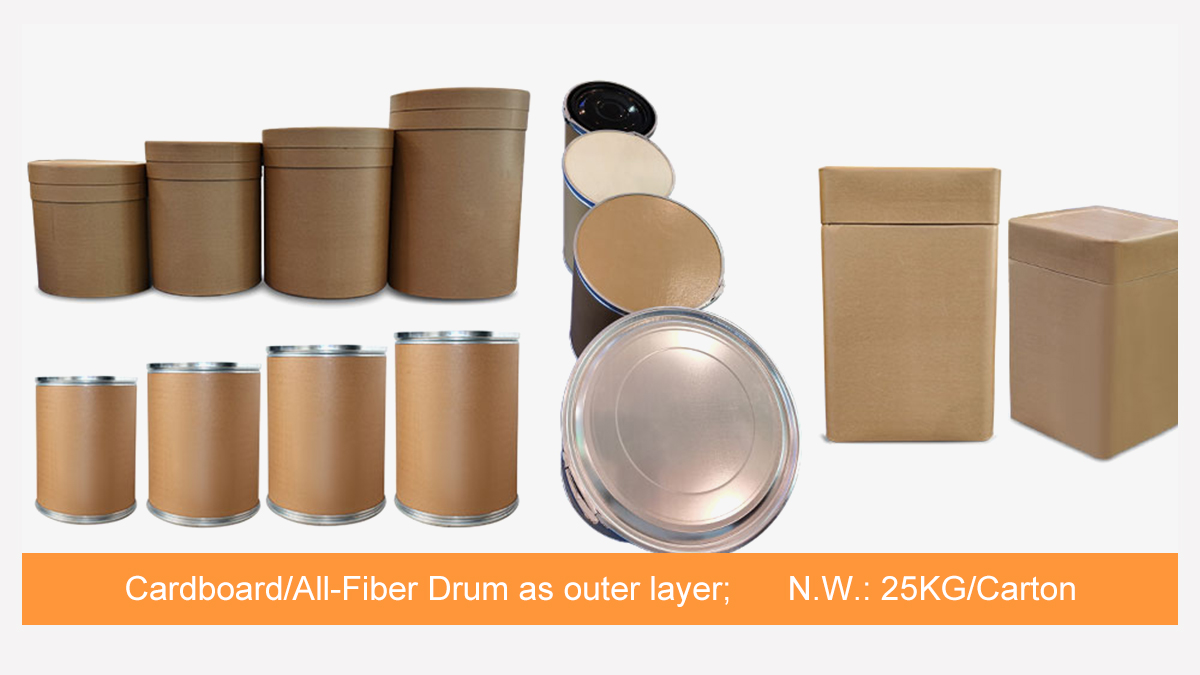
Lotus Leaf Extract
Latin Name: Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn
Spec: 2% Nuciferine HPLC
Description
In Chinese medicine, the lotus leaf is classified as a bitter herb. According to traditional practitioners, bitter herbs trigger the production of bile and hydrochloric acid, effects which stimulate digestion and ease flatulence. Bile secretion assists in the breakdown of fats, and serves as a liver tonic. According to traditional Chinese medicine, lotus leaf stimulates the liver and spleen meridians. As an astringent, lotus leaf has the ability to stop bleeding, and is used to treat conditions such as hematuria (blood in urine), hematemesis (blood in vomit) and metorrhagia (excessive menstrual bleeding).


Lotus Leaf Extract
Latin Name: Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn
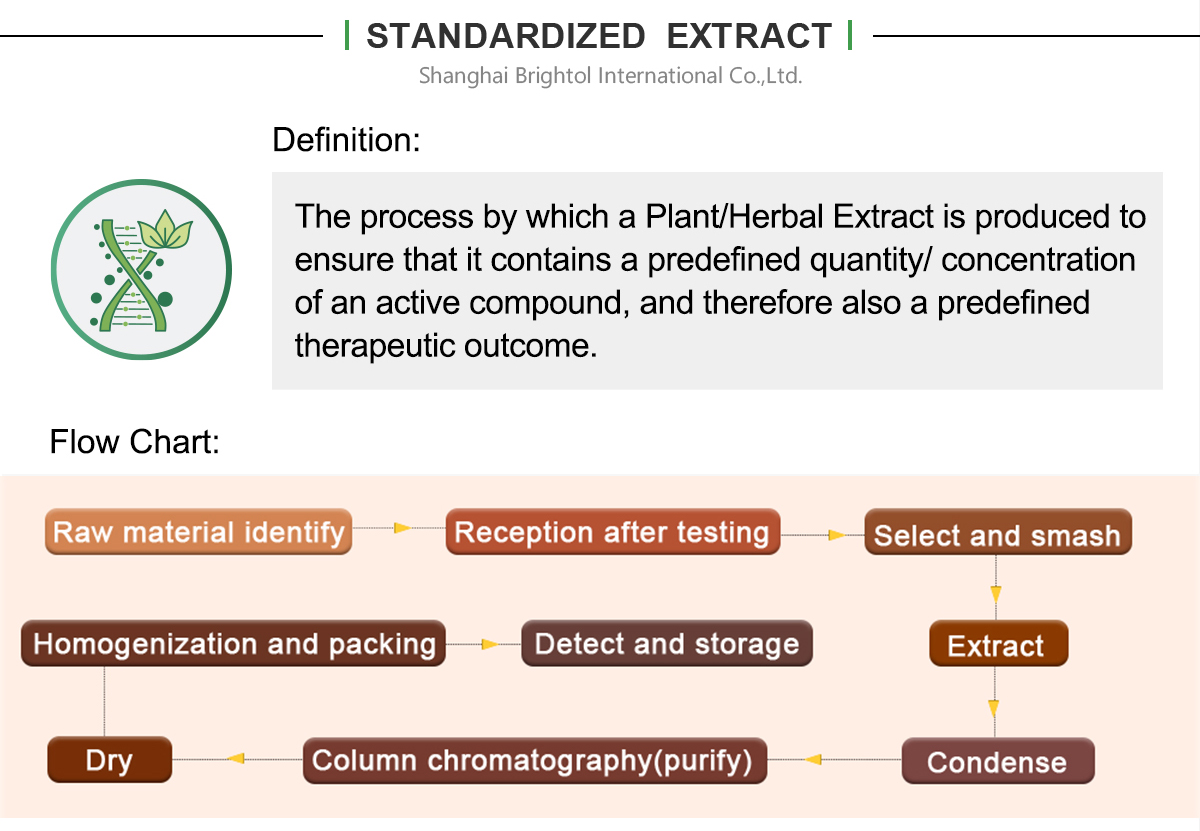
Spec: 2% Nuciferine HPLC
Description
In Chinese medicine, the lotus leaf is classified as a bitter herb. According to traditional practitioners, bitter herbs trigger the production of bile and hydrochloric acid, effects which stimulate digestion and ease flatulence. Bile secretion assists in the breakdown of fats, and serves as a liver tonic. According to traditional Chinese medicine, lotus leaf stimulates the liver and spleen meridians. As an astringent, lotus leaf has the ability to stop bleeding, and is used to treat conditions such as hematuria (blood in urine), hematemesis (blood in vomit) and metorrhagia (excessive menstrual bleeding).
Benefit
Lotus leaf contains alkaloids, flavonoids and tannins. The isoquinoline alkaloids in the leaf have sedative and antispasmodic properties, which may aid in digestion, and the flavonoids and tannins, are powerful antioxidants which protect the heart and assist in weight loss.