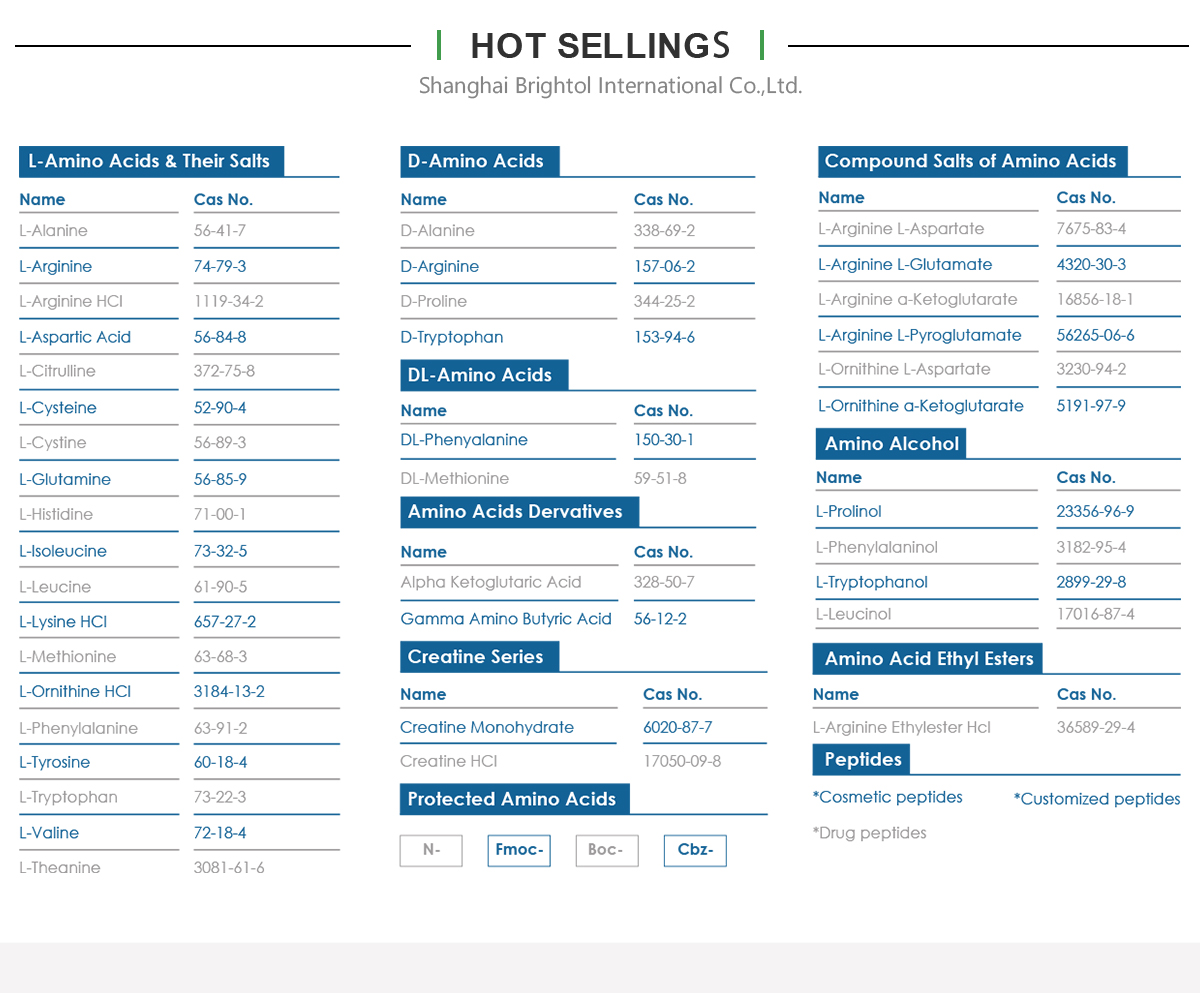
Product Name: L-Glutamine
Synonyms: 2-Aminoglutaramic acid;
Levoglutamide; L(+)-Glutamic acid-5-amide
Molecular Formula: C5H10N2O3
Molecular Weight: 146.14
CAS No.: 56-85-9
EINECS: 200-292-1
FEMA: 3684
Description
Glutamine is one of 20 naturally occurring amino acids in dietary protein. In fact, L-glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the bloodstream and makes up 30–35 percent of the amino acid nitrogen in your blood. It’s actually known as a conditionally essential amino acid because your body uses it in large amounts.


Product Name: L-Glutamine
Synonyms: 2-Aminoglutaramic acid;
Levoglutamide; L(+)-Glutamic acid-5-amide
Molecular Formula: C5H10N2O3
Molecular Weight: 146.14
CAS No.: 56-85-9
EINECS: 200-292-1
FEMA: 3684
Description
Glutamine is one of 20 naturally occurring amino acids in dietary protein. In fact, L-glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the bloodstream and makes up 30–35 percent of the amino acid nitrogen in your blood. It’s actually known as a conditionally essential amino acid because your body uses it in large amounts.
What does ‘conditionally essential amino acid’ mean? It refers to the amino acid becoming essential when the individual faces disease or specifically muscle wasting, which can happen in the course of certain diseases or even physical trauma. It also becomes a conditionally essential nutrient during certain catabolic states, including after bone marrow transplantation.
Found in both animal and plant proteins, it’s also available in supplement form and is widely popular in the fitness community and beyond. It’s found in high levels in both casein and whey protein.
Benefits
1) Improves gastrointestinal health
2) Helps leaky gut and ulcers
3) Boosts brain health
4) Improves IBS and diarrhea
5) Promotes muscle growth and decreases muscle wasting
6) Improves athletic performance and recovery from endurance exercise
7) Burns fat and improves diabetes